AppCode
This high-quality and hand-picked collection shows CSS carousel examples from across the web. Included are examples and code for reuse.
Related
Pure CSS Classy Footer
About Project
Simple Fixed Footer
About Project

Simple Slide-Out Footer
About Project

Simple Responsive Fixed Footer
About Project

Animated Mobile Footer Menu
About Project
Social Media Footer
About Project
Footer With Conent Scale
About Project

Parallax Footer (Website Fixed Footer)
About Project

Flexbox Sticky Footer Example
About Project
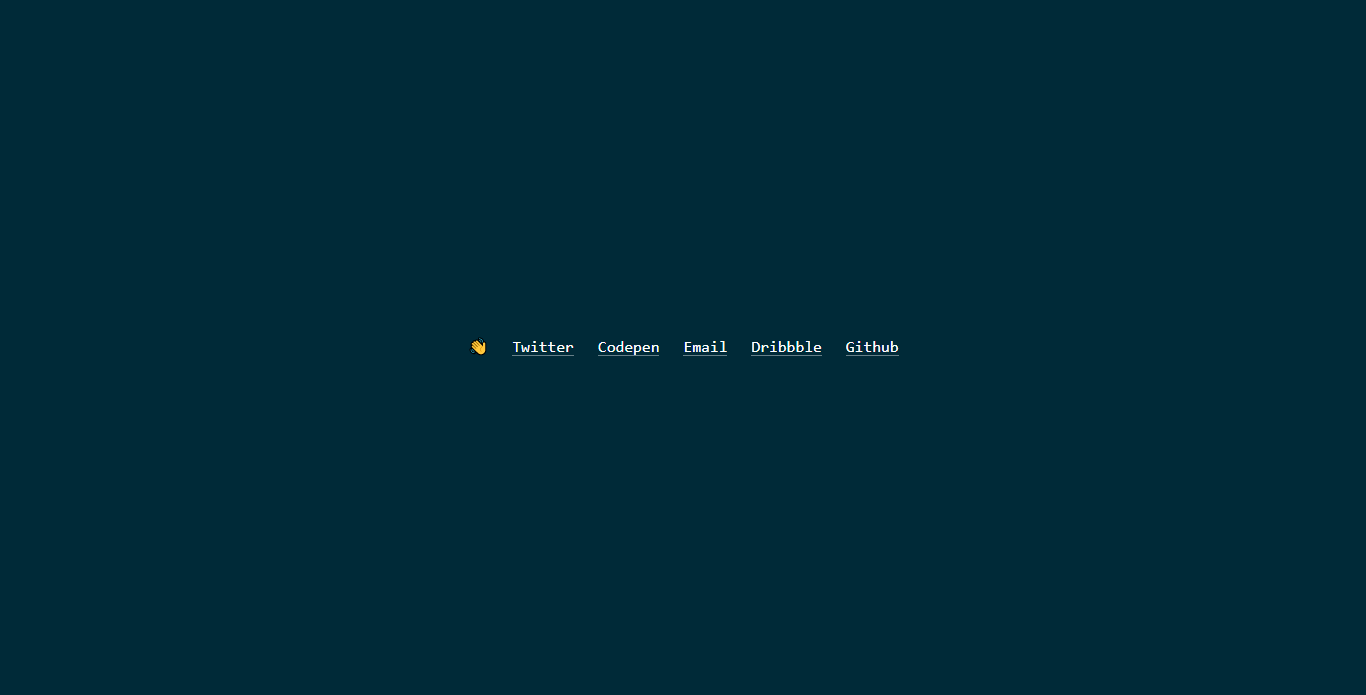
Footer with CSS Grid
About Project
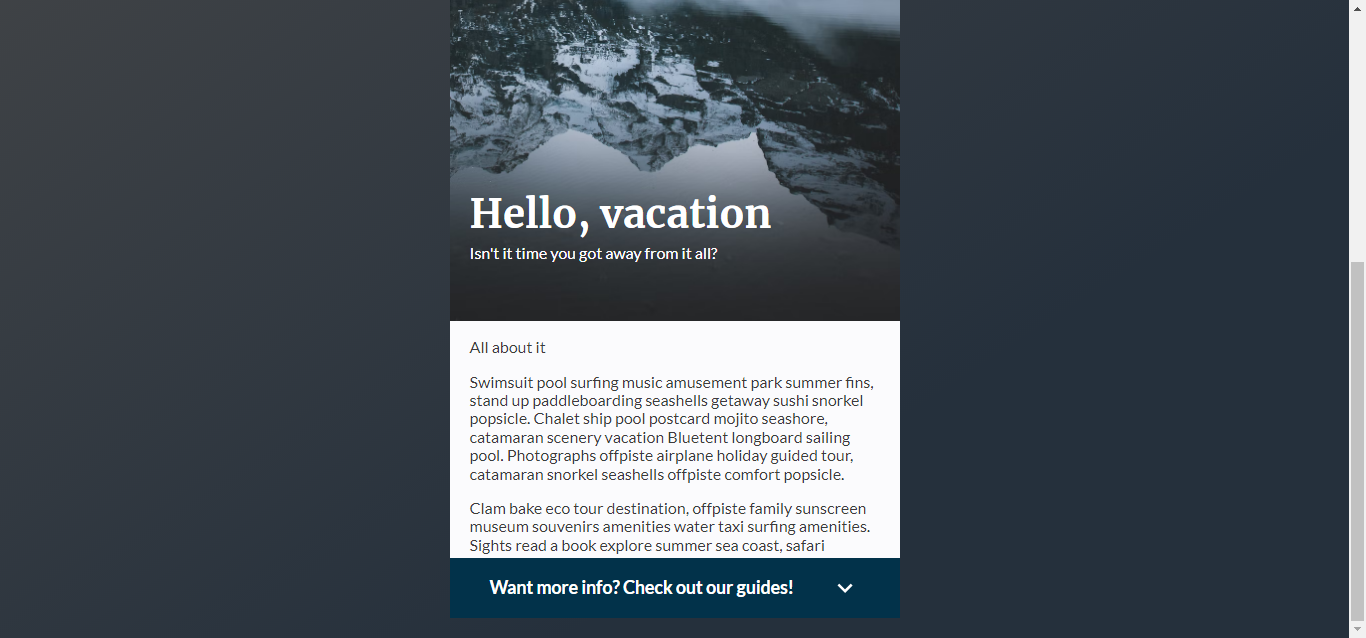
Animated Footer Toggle
About Project

Footer Always at the Bottom – Flexbox
About Project

Bubble-Type CSS Goey Footer
About Project
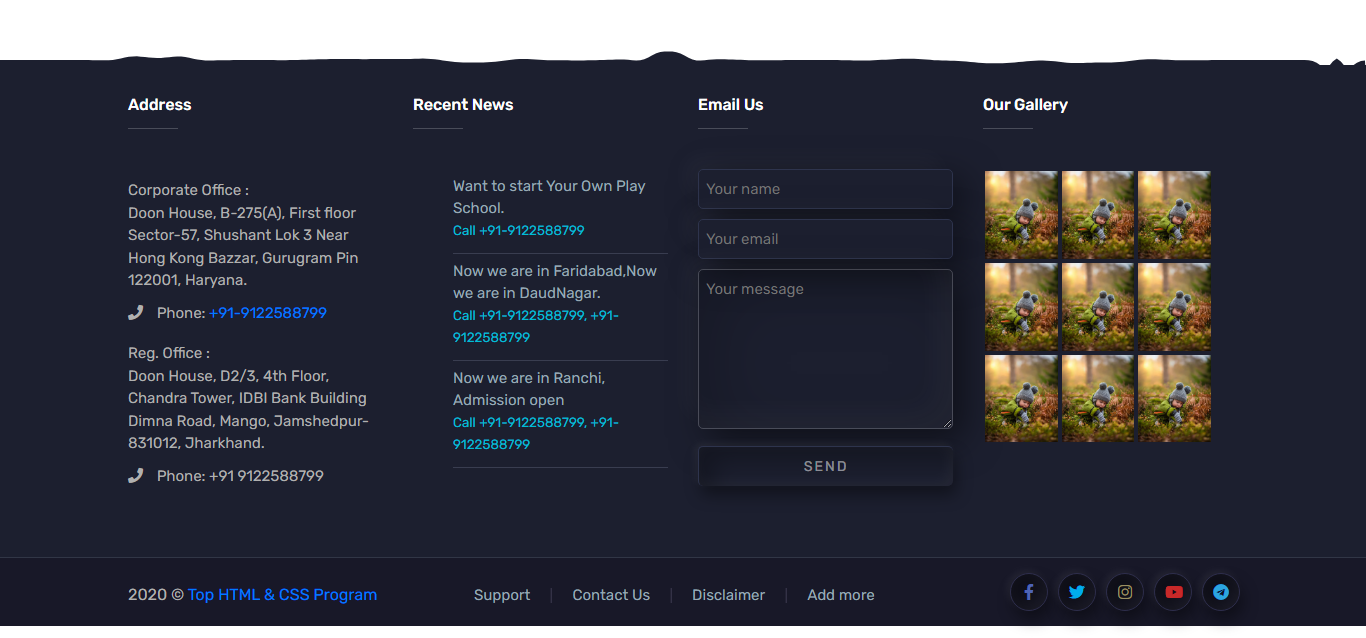
Footer Design With Embossed Effect
About Project

CSS “Always on the Bottom” Footer
About Project
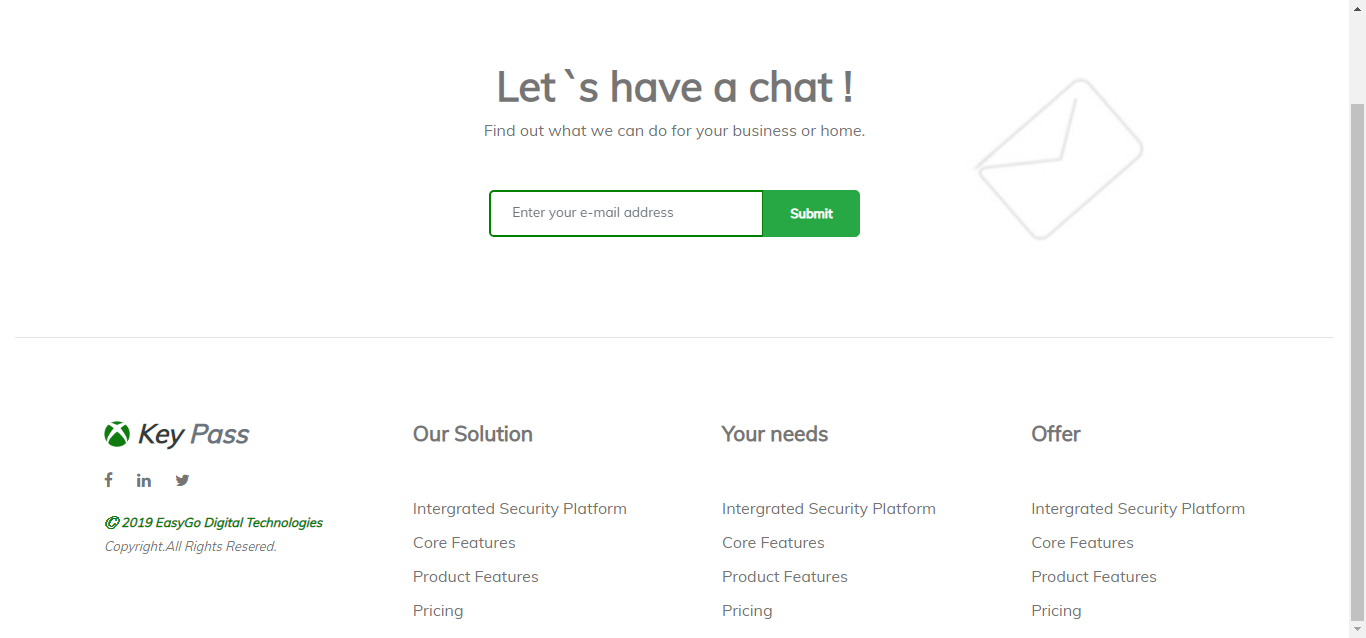
Bootstrap Footer 6(Source From Bootstrap)
About Project
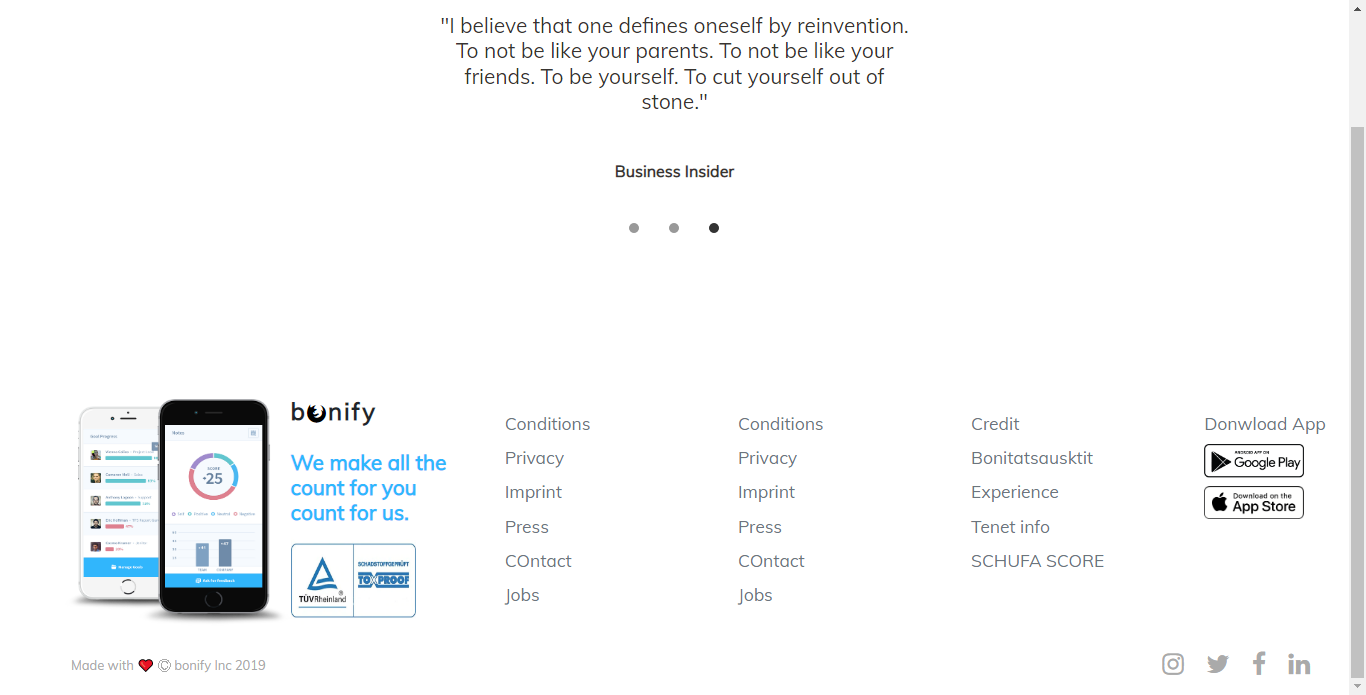
Bootstrap Footer 5 (Source From Bootstrap)
About Project
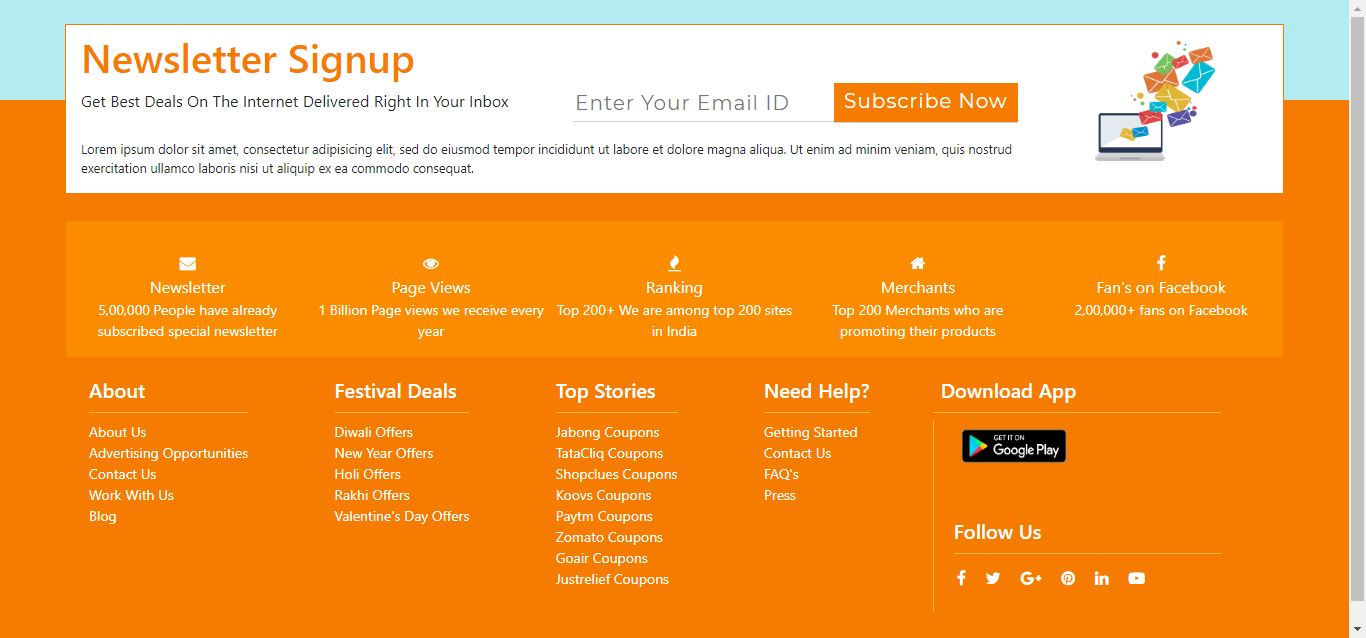
Bootstrap Footer 4 (Source From Bootstrap)
About Project
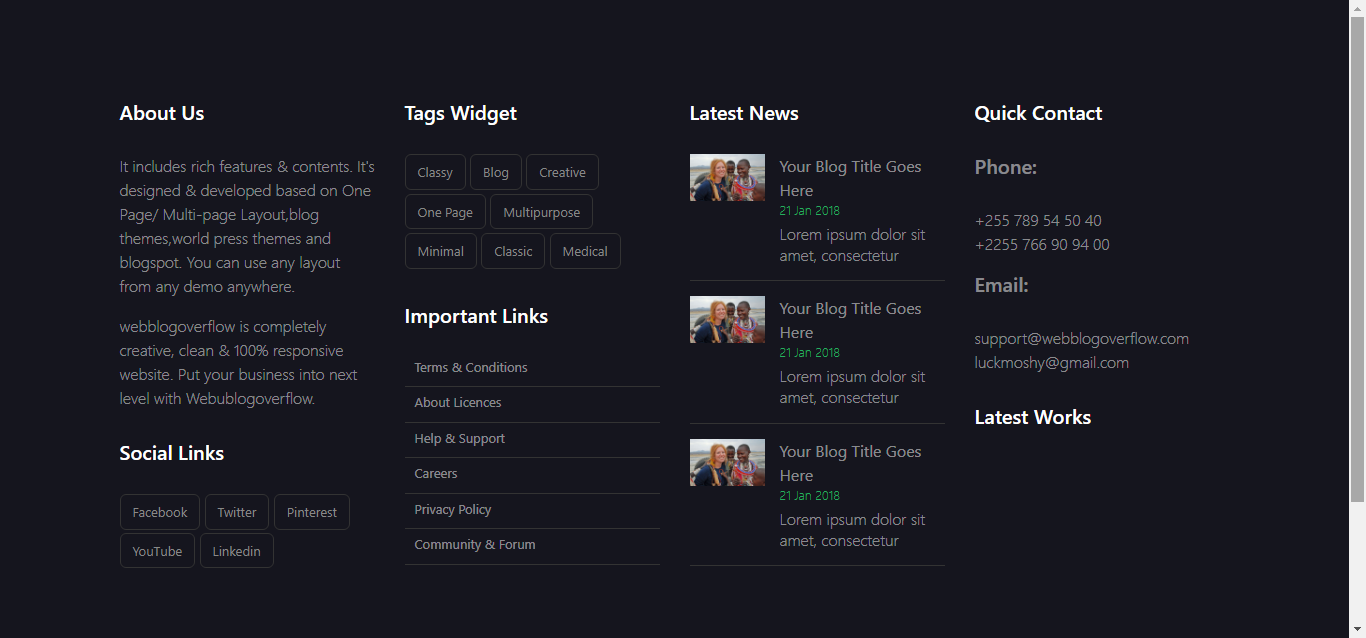
Bootstrap Footer 2 (Source From Bootsnipp)
About Project
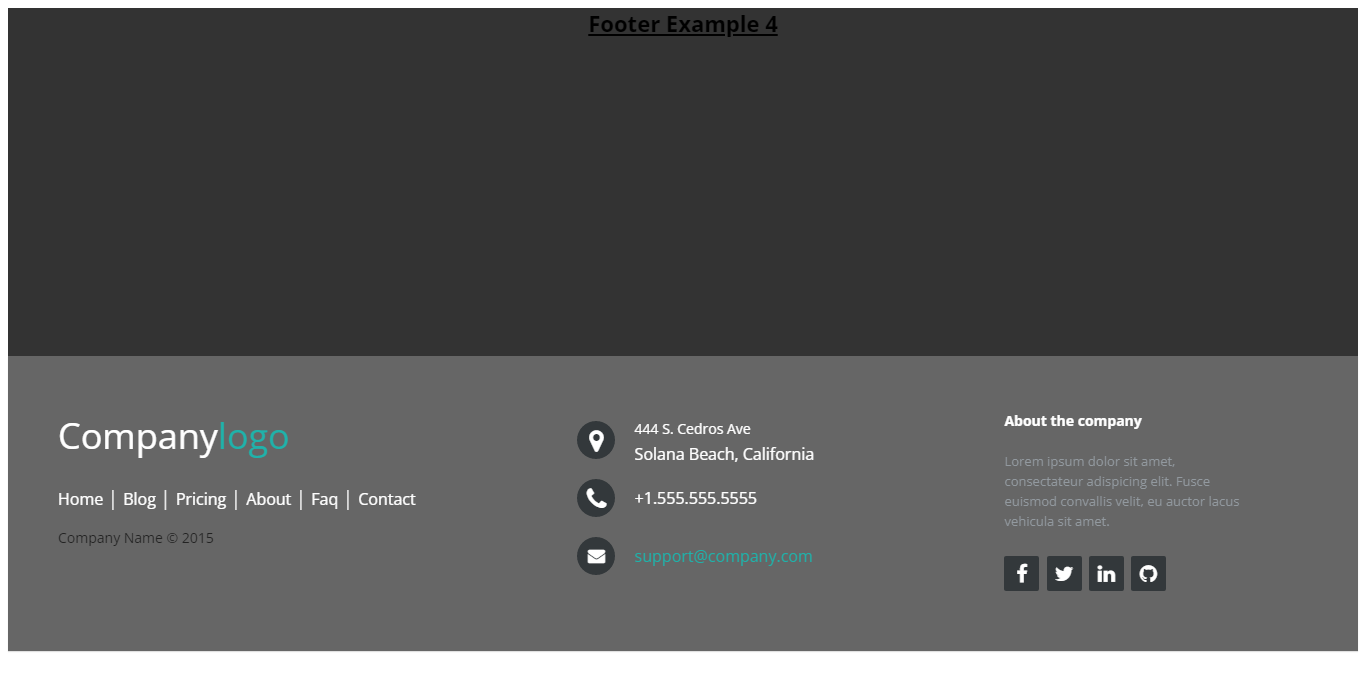
Footer With Company Logo
About Project
Footer Template With Category
About Project
Template Contact & Footer
About Project
Footer Using Bootstrap 4(Source From Bootsnip)
About Project
Bootstrap Footer With Company Logo 2
About Project
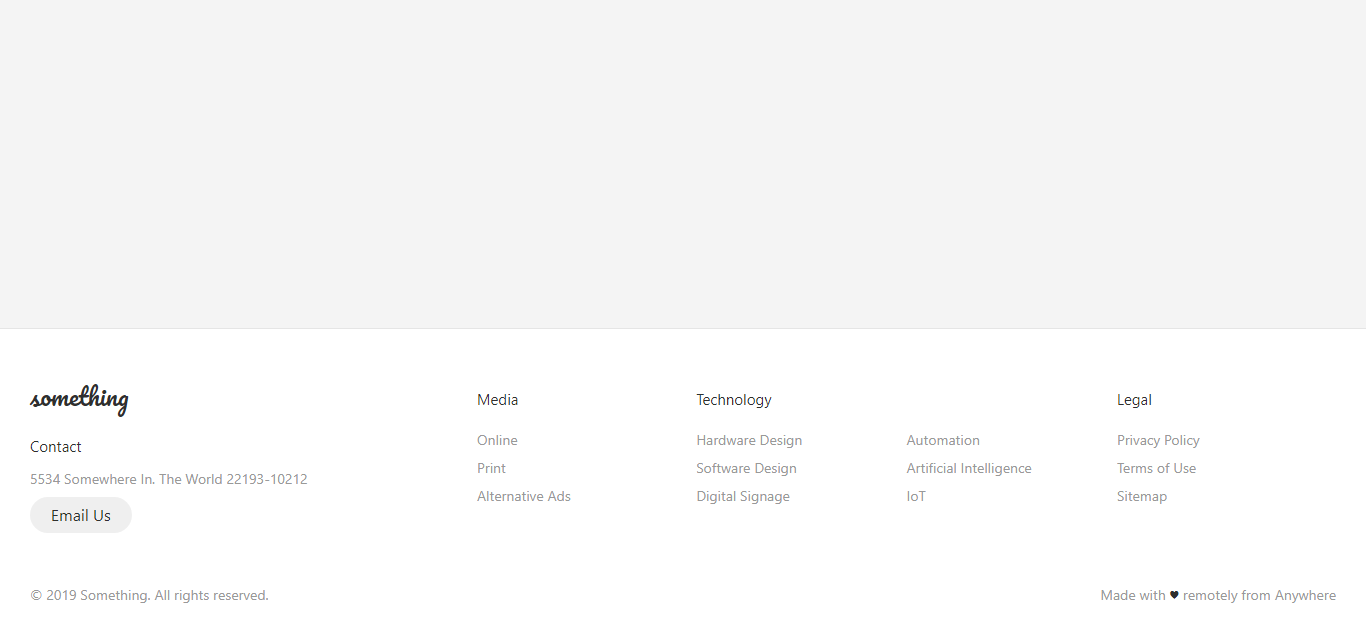
Responsive Flexbox Footer
About Project
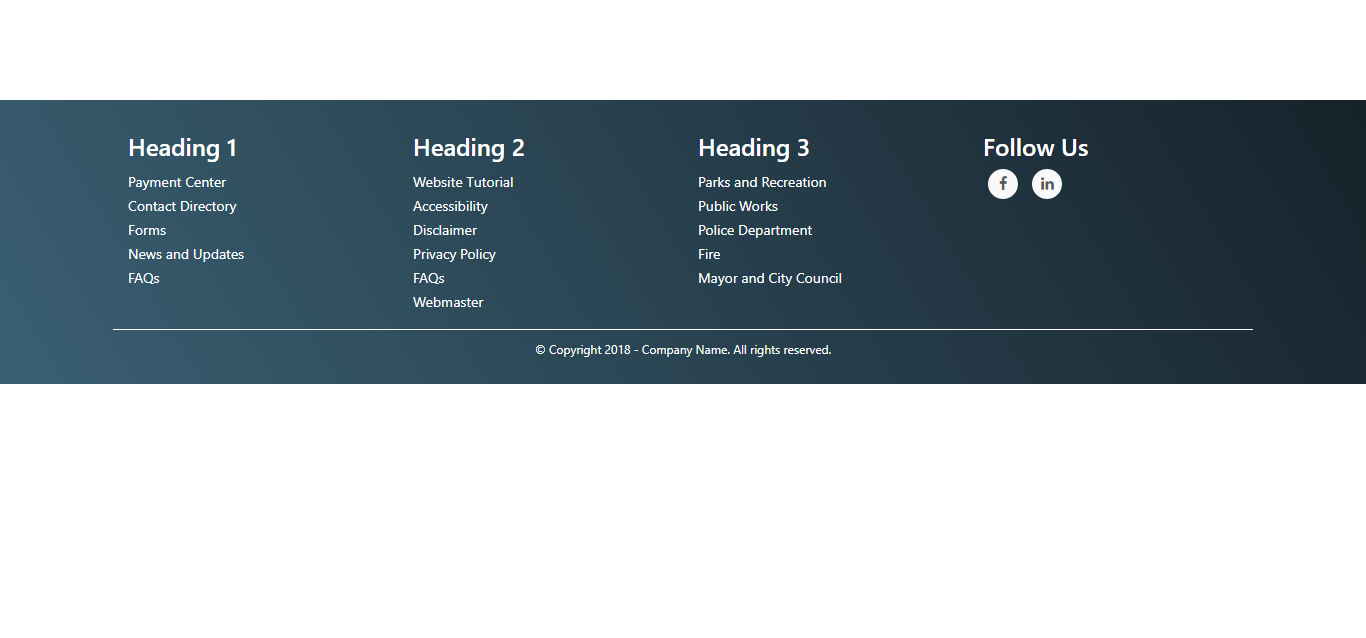
Bootstrap 4 Footer With Social Icons
About Project
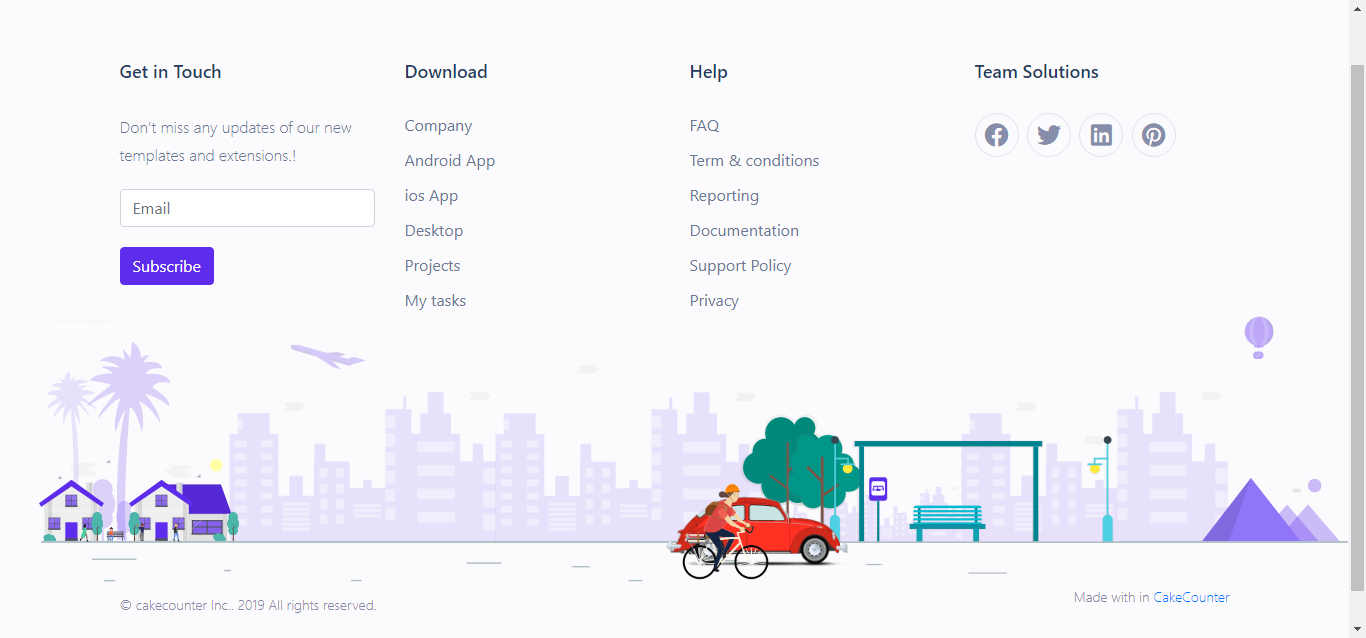
Stylish Footer With Animation
About Project

Just Another Simple Footer
About Project
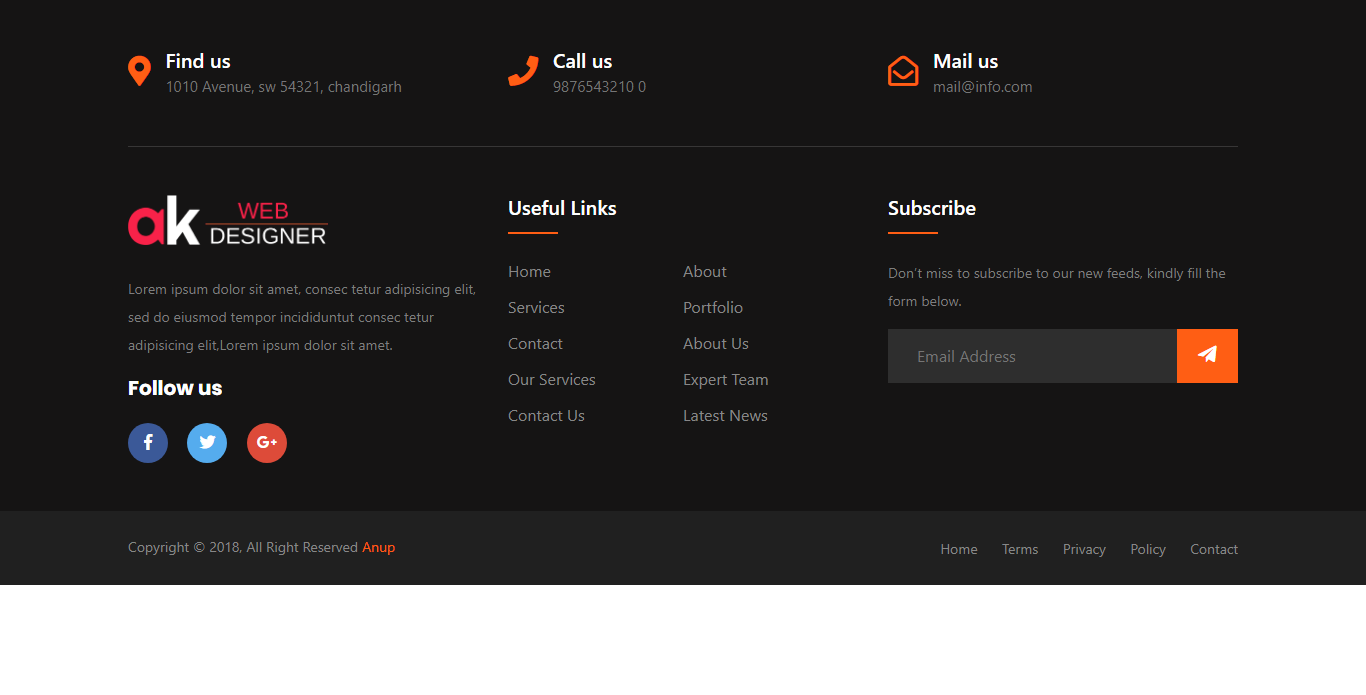
Footer Responsive
About Project
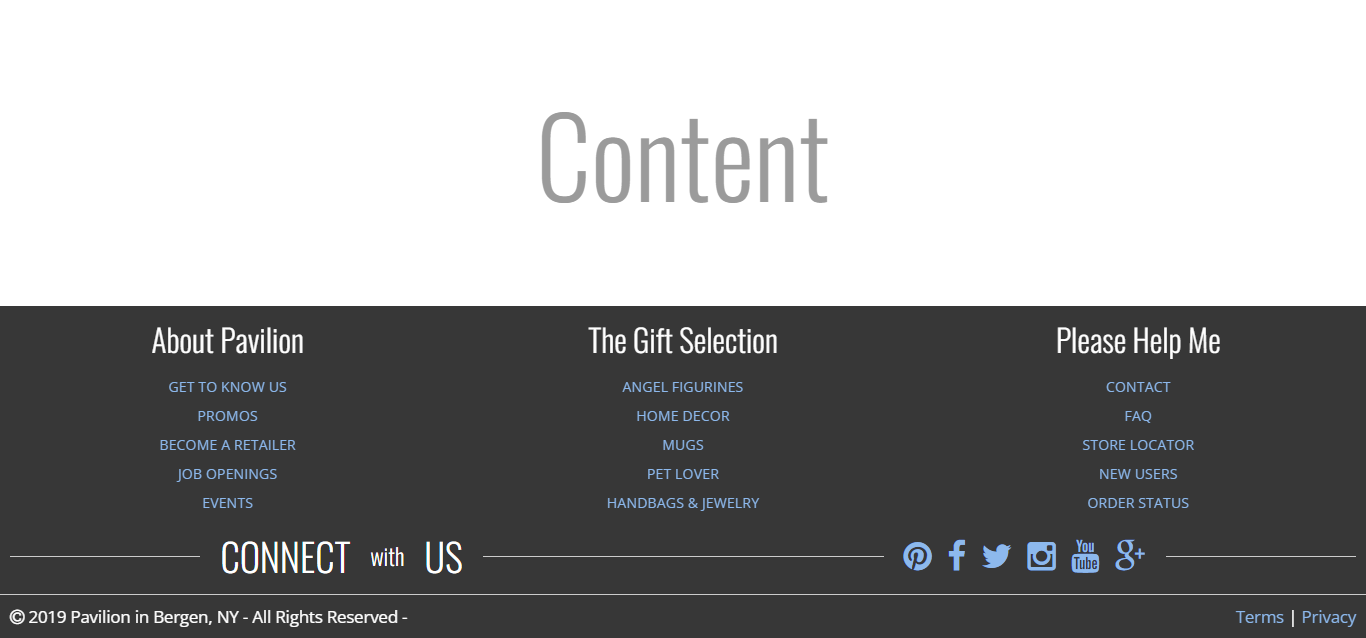
Responsive & Clean Footer Design
About Project

Attractive Responsive Footer
About Project
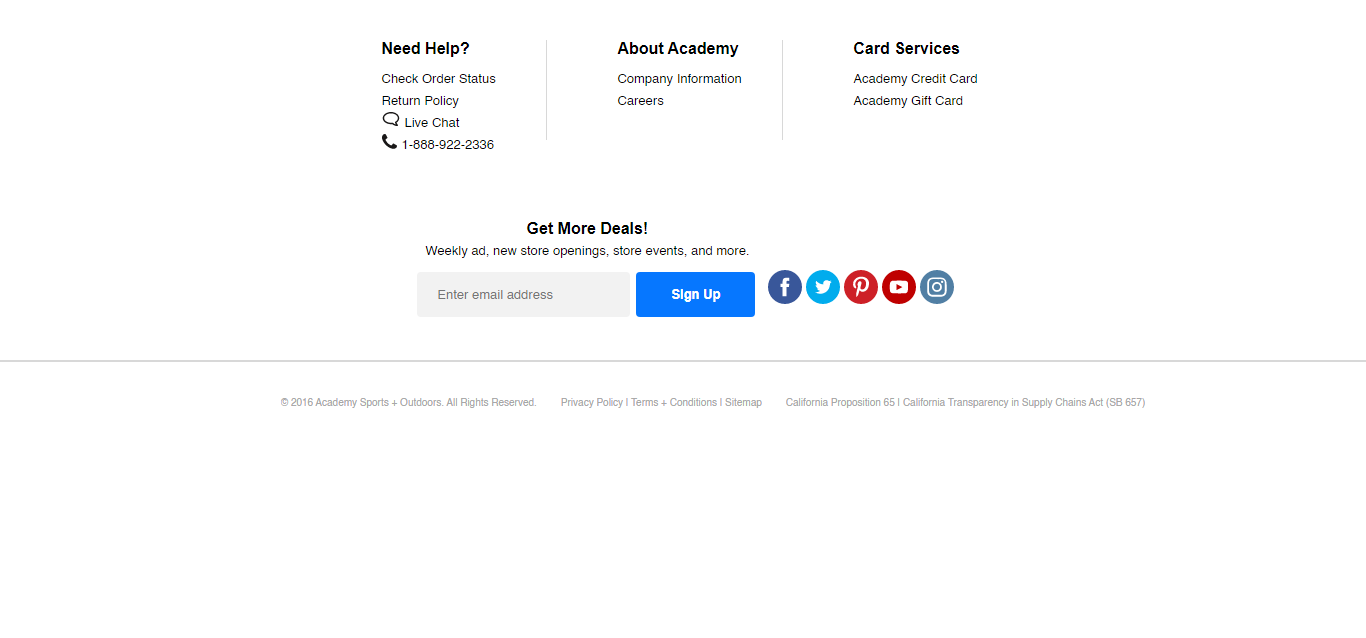
3 Blocks Responsive Footer
About Project
Recommended Articles
- 32 CSS Carousel Examples and Code
- 15 Flexbox CSS Examples and Code
- 32 CSS Page Transition Examples and Code
- 32 CSS Form Examples and Code
- 32 CSS Tab Examples and Code
- 33 CSS Button Examples and Code
- 32 CSS Search Box Examples and Code
- 32 CSS Mobile Menu Examples and Code