Google Rank Factors to improve traffic. A complete list of backlinks, page-level factors, domain factors, google algorithm factors, google SEO, and more.
- Domain Factors
- Page Level Factors
Domain Factors
1. Domain Age: The length of time a domain has been active is a factor in Google search ranking.
2. Keyword in Top Level Domain: When a keyword is in the top-level domain it gives you an SEO boost and is a point in the factoring system Google uses to rank webpages. For example, if your domain has SEO in the domain, seo-ranker.com, then this counts as a relevancy signal.
3. Keyword Position in Top Level Domain: The position of keywords in the top-level domain provides another factor in the google search algorithm. When you search SEO rank, then if your domain is seo-rank.com will provide a better match than rank-seo.com. See the difference in position, haha?
4. Domain Registration Length: The longer a domain is registered for indicates a less spamming domain. More important domains are registered longer, like apple.com vs a random spam domain.
5. Keyword in Subdomain: Another factor google uses is if the keyword is in the subdomain. Hence seo.rank.com would be a valid factor if someone searches for “SEO rank” keywords.
6. Exact Match Domain: A domain as an exact match is a better search result than a domain that isn’t. If you search cats you wouldn’t expect dogs.com to be on the first page of results.
7. Domain History: A domain with a history of a lot of transfers indicates the domain structure or content changes often vs a steady domain with a long-time owner.
8. Public vs Private WhoIs: A domain without privacy protection indicates more transparent domain ownership vs a domain that hides their information. Spam domains quite often set up privacy protection to hide the owner of the domain.
9. WhoIs Private Penalty: Owers of a domain, who’s domain has been penalized may end up having all their domains penalized.
10. Country TDL Extention: Domains with specific TDL extensions like .au (Australia), .us (United States), or even .cn (China) will quite often rank better in those locations.
11. Hyphenated Domains: Domains hyphenated like seo-rank.com vs seorank.com might fare better in google search results due to the better visibility from the user who performs the search.
Page Level Factors
12. Keyword in Title Meta Tag: Keyword in the title meta tag is an important ranking factor when building a page towards a specific keyphrase.
13. Keyword in H1 Tag: Having the keyword in the H1 tag is a great relevancy signal to google’s indexing spider.
14. Keyword in H2 Tag: Including the keyword or keyphrase in the HTML element H2 tag is another ranking factor.
15. Keyword in Subsequent Headings: When the key phrase is included in additional headings like H3, H4, and H5, they are also indicating factors that the page content is relevant to the user’s query.
16. TF-IDF: TF-IDF stands for “Term Frequency — Inverse Document Frequency”. This is a technology used to quantify the word in a document. This reflects the importance of a word in the document. This is a very important factor to determine if the content is relevant to a search query.
17. Content-Length: The content length of a document is an important relevancy signal. This shows that the document covers more areas on the keyword that it is written for. In other words, a small 200-word page has less information on a topic compared to a much larger 4000-word document.
18. Table of Contents: Using a table of contents that links to anchors in a page may result in special google search site links.
19. Keyword Density: The focus keyword density in a document is an important Google algorithm factor this relates to the TF-IDF of a document. Having one keyword in a document does not signify that the page is relevant to the term a user is searching for.
20. Latent Semantic Indexing Keywords in Content(LSI): LSI keywords are terms and phrases similar or related to the page’s focus keyword. This helps search engines understand the context of a document.
21. LSI Keywords in Title and Description Tags: LSI in the title meta and description tags are important factors in connecting the relevancy of the document to the keyword or keyphrase.
22. Page Covers Topic In-Depth: The depth of a topic on a page directory correlates with improved google search rank vs a page that only partially covers a topic.
23: Page Load Speed: Most search engines use page load speed as a ranking factor. The faster the webpage then the more likely it will show higher in the search results.
24. Server Response Time: The time it takes for a server to respond to a request is part of the page load speed ranking factor. If a server takes a shorter amount of time to process a request, then a browser can start the page loading process as it received all or some parts of the page.
25. Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP):Using AMP in your website will help improve the search ranking of a website by allowing a page to show up in google’s preview carousel in mobile search.

26. Entity Match: Another major ranking factor is if the document matches the entity, object or person, a user is searching for.
27. Google Hummingbird: The google Hummingbird update gives more importance to the context and meaning of a document instead of keywords and phrases. This update allows the search engine to have a deeper understanding of the topic to direct users to the appropriate page.
28. Duplicate Content: Having duplicate content on a site negatively impacts visibility in search engines.
29. Rel=Canonical: If Google sees multiple URLs pointing to the same content or slightly modified content related to the original content, then google treats everything but the first URL as duplicate content. Rel=Canonical solves this by pointing to one URL. Using the Rel=Canonical tag can consolidate similar content and URLs referring to the same content by pointing to a single canonical URL.
30. Image Optimization: Delivering payload optimized images is a ranking factor as this tells Google that the images can be loaded fast and delivered to the user for consumption.
31. Image Filename: Search engines reading the image filename can tell the engine what the file is about.
32. Image Alt Text: Alt Text can describe the image to Google.
33. Image Caption: The image caption is another important ranking factor as this is a brief explanation of the image.
34. Image Title: The image title is the title of the image. Google uses this sometimes to display rich images in mobile and desktop search results.
35. Image Description: The image description is similar to the image caption but typically longer in length. This is a very important signal to Google that the content of a page is more relevant by having images that support the document.
36. Content Recency: Googles’s Caffeine update introduced a search new content indexing system. The old indexing system that it replaced was a layered system. This layered system was refreshed… in well… layers. So results provided through the engine were layered. Caffeine on the other hand indexes new and updated content on the web as soon as it’s found. New and updated content can increase the ranking factors of a site.
37. Magnitude of Content Updates: The amount of edits and changes to a document carries greater significance than a couple of tweaks, type fixes, or image insertions.
38. Historical Page Updates: The frequency of updated content over time can contribute to better search ranking as this signifies that the is fresh and updates often.
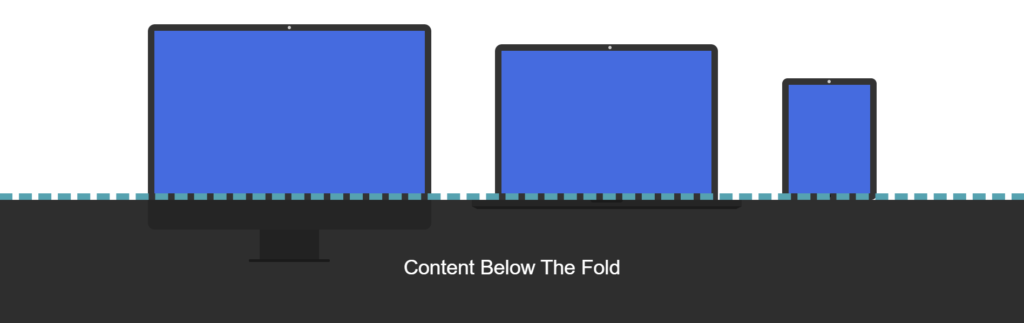
39. Content Below The Fold: Having the most important information of a page above the fold vs below the fold is a significant factor in ranking. When the information is above the fold, the information is readily available to the user on page load.